-
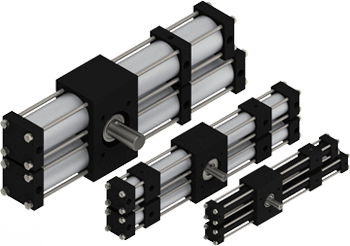
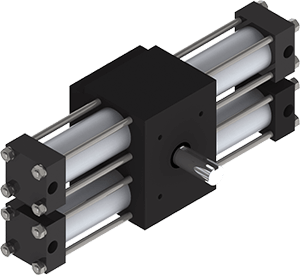
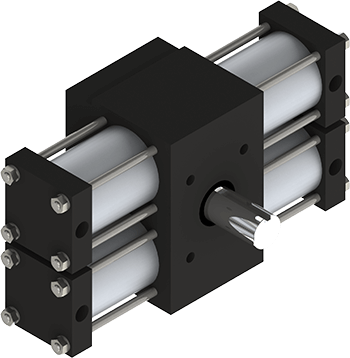
 Rotary Rotary ActuatorsCompactA032*80psi
Rotary Rotary ActuatorsCompactA032*80psi Torque: 9 in-lb*
Torque: 9 in-lb*
Shaft: 1/4" or 3/8"
DiameterAL75*80psi Torque: 7-14 in-lb*
Torque: 7-14 in-lb*
Shaft: 1/4"
DiameterA752*80psi Torque: 35 in-lb*
Torque: 35 in-lb*
Shaft: 3/8"
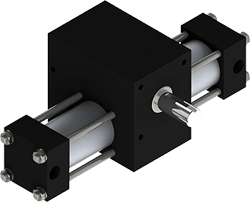
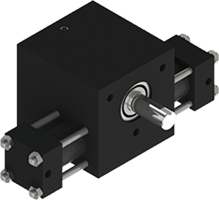
DiameterSingle Rack Tie-RodA01*80psi Torque: 6 in-lb*
Torque: 6 in-lb*
Shaft: 3/16" or 1/4"
DiameterA1*80psi Torque: 12 in-lb*
Torque: 12 in-lb*
Shaft: 1/4" or 3/8"
DiameterA2*80psi Torque: 39 in-lb*
Torque: 39 in-lb*
Shaft: 1/2"
DiameterA3*80psi Torque: 119 in-lb*
Torque: 119 in-lb*
Shaft: 3/4"
DiameterA4*80psi Torque: 277 in-lb*
Torque: 277 in-lb*
Shaft: 1" or 1 1/8"
DiameterDual Rack Tie-RodA12*80psi Torque: 24 in-lb*
Torque: 24 in-lb*
Shaft: 1/4" or 3/8"
DiameterA22*80psi Torque: 78 in-lb*
Torque: 78 in-lb*
Shaft: 1/2"
DiameterA32*80psi Torque: 238 in-lb*
Torque: 238 in-lb*
Shaft: 3/4"
DiameterA42*80psi Torque: 545 in-lb*
Torque: 545 in-lb*
Shaft: 1" or 1 1/8"
Diameter -
 Multi-Position Multi PositionThree Position ActuatorsA032*80psi
Multi-Position Multi PositionThree Position ActuatorsA032*80psi Torque: 6 in-lb*
Torque: 6 in-lb*
Shaft: 1/4" or 3/8"
DiameterA12*80psi Torque: 12 in-lb
Torque: 12 in-lb
Shaft: 3/8"
DiameterA22*80psi Torque: 39 in-lb*
Torque: 39 in-lb*
Shaft: 1/2"
DiameterA32*80psi Torque: 119 in-lb*
Torque: 119 in-lb*
Shaft: 3/4"
DiameterA42*80psi Torque: 277 in-lb*
Torque: 277 in-lb*
Shaft 1 or 1 1/8"
Diameter4 or 5 Position ActuatorsFour or Five Position*80psi Torque: 12-277 in-lb*
Torque: 12-277 in-lb*
Shaft: 3/8"-1 1/8"
Diameter -
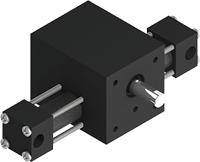
 Indexing Indexing ActuatorsSingle RackX1*60psi
Indexing Indexing ActuatorsSingle RackX1*60psi Torque: 9 in-lb*
Torque: 9 in-lb*
Shaft: 3/8*
DiameterX2*60psi Torque: 29 in-lb*
Torque: 29 in-lb*
Shaft: 1/2"
DiameterX3*60psi Torque: 89 in-lb*
Torque: 89 in-lb*
Shaft: 3/4"
DiameterX4*60psi Torque: 208 in-lb*
Torque: 208 in-lb*
Shaft: 1"
Diameter -
 Stepping
Stepping -
 Multi-Motion
Multi-Motion -
 Nitpicker Nitpicker ActuatorsSingle RackPX2*80psi
Nitpicker Nitpicker ActuatorsSingle RackPX2*80psi Torque: 39 in-lb*
Torque: 39 in-lb*
Shaft: 1"
Diameter -
 Shaft Mounting Adapters
Shaft Mounting Adapters
Linear vs. Rotary Actuators: Which is Best for My Application?
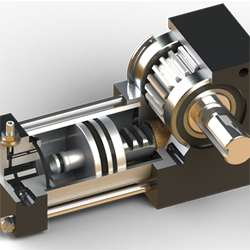
Actuators are integral components of machines, converting energy into motion. They come in different types, but the two most used are linear and rotary actuators. Choosing between these two can be a daunting task, especially if you’re not familiar with their characteristics and applications. To help you make an informed decision, let’s delve into the world of linear and rotary actuators.
What are Linear and Rotary Actuators? Linear actuators create motion in a straight line, contrary to the circular motion produced by rotary actuators. In essence, linear actuators move objects up and down or back and forth, while rotary actuators turn objects around a fixed point.
Linear Actuators Linear actuators are a versatile solution for machinery that requires precise linear motion. Whether it’s adjusting control surfaces on an aircraft or positioning a cutting head, linear actuators offer direct linear motion with advantages like precise positioning, low power consumption, and easy control. They provide the necessary movement in a straight line, ensuring efficient operation in various applications. With their ability to deliver accurate and controlled linear motion, linear actuators prove to be a reliable choice for tasks that demand precision and efficiency.
Rotary Actuators When it comes to rotational motion around an axis, rotary actuators are the go-to choice. Whether it’s rotating a conveyor belt or turning a valve, these actuators excel in providing high torque and ensuring smooth and continuous rotation. It’s worth noting that there are different types of rotary actuators available. Some, like motors, offer unlimited rotation, while others like pneumatic or hydraulic rotary actuators have limited rotation. Regardless of the type, rotary actuators boast a compact design, allowing for efficient operation at high rotational speeds. With their impressive capabilities, they are a reliable solution for tasks that require precise and powerful rotational motion.
Choosing Between Linear and Rotary Actuators
When deciding between a linear and rotary actuator, consider the following aspects:
Application Requirements: What type of motion does your application need? If it’s linear, a linear actuator will be the best choice. If it’s rotational, then a rotary actuator will be more suitable.
Space Constraints: Rotary actuators are generally more compact and better suited for applications with limited space.
Cost: Price can also be a determining factor. Generally, linear actuators are less expensive than rotary ones, but this can vary based on specific models and manufacturers.
Control System Compatibility: Ensure that the actuator you choose is compatible with your existing control system.
In conclusion, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer to whether a linear or rotary actuator is better. It largely depends on the specific requirements of your application. By understanding the key differences and considering the factors mentioned above, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs. Remember, the right actuator can significantly enhance the efficiency and performance of your machine or system.